


I will begin the article by answering 5 commonly asked questions about China.
Located in East Asia China is not a land locked country that up until recently had the world’s largest population. China’s many land borders include North Korea, Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Laos, and Vietnam. Just looking at the sheer amount of borders China has you can tell how massive the country is without even having to look at a map. China also holds the record for most land borders, and we will expand on all of them later in the article.
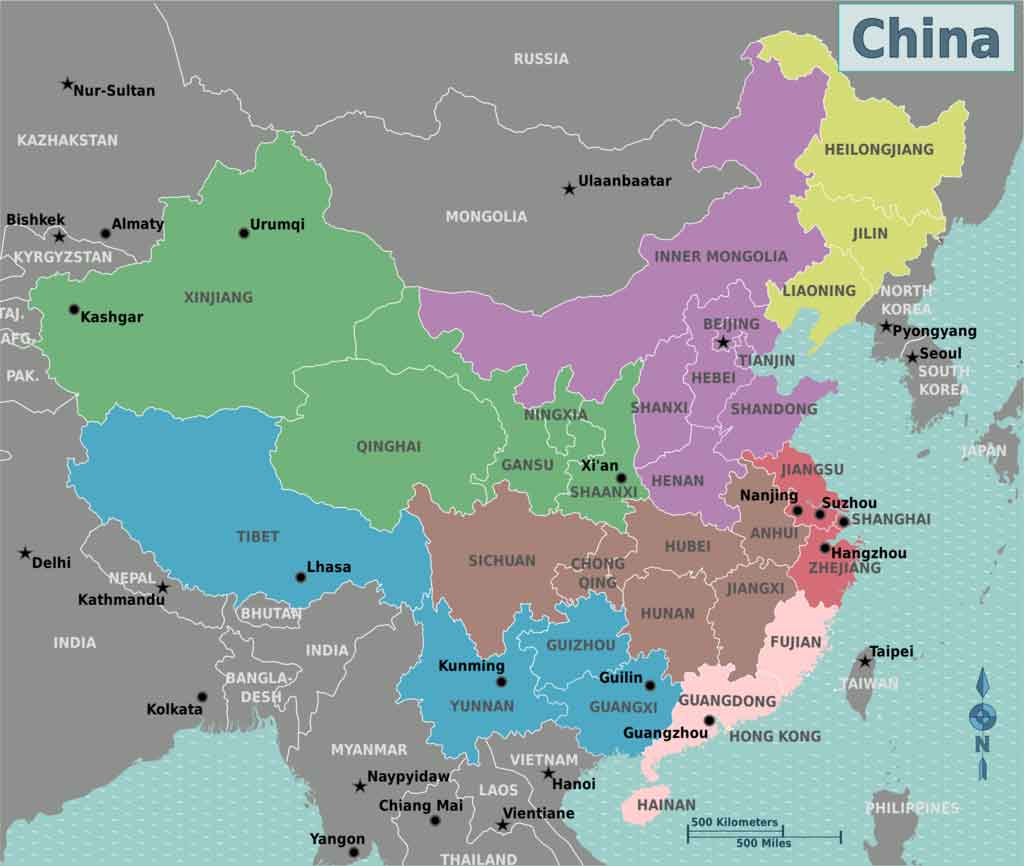
China is then divided into 23 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities directly under the central government, and two special administrative regions.
China’s flag features a red background with five yellow stars arranged in a five-pointed pattern in the upper-left corner. There are four smaller stars surround a larger central star, which represents the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the unity of the Chinese people under CCP leadership.
The red colour of the flag symbolizes the revolution and the bloodshed of the Chinese people in their struggle for independence and national liberation. And as previously mentioned, the five stars on the flag represent the unity of the Chinese people, under the leadership of the CCP, with the goal of achieving peace, progress, and prosperity. The current design of the flag was officially adopted on September 27, 1949, shortly after the establishment of the People’s Republic of China.

The official currency used in China is the Chinese yuan, which is also known as the renminbi (RMB). The yuan is further divided into units called “jiao” and “fen”, with one yuan equal to 10 jiao and one jiao equal to 10 fen. However, the use of fen is rare these days due to inflation, and jiao is used more commonly in day to day transactions. The yuan is issued by the People’s Bank of China, which is the central bank of the country, and is used throughout mainland China. The ISO code for the Chinese yuan is “CNY”.
The yuan is issued in banknotes and coins, with the banknotes coming in denominations of 1, 5, 10, 20, 50, and 100 yuan, and the coins in denominations of 1 yuan and smaller denominations called jiao (0.1 yuan) and fen (0.01 yuan), although as previously mentioned coins smaller than 1 yuan are rarely used these days.
China’s official language is Standard Mandarin, it is also known as Putonghua or as it is widely known as in the West it is simply referred to as just “Chinese”. It is a standardized form of the Mandarin dialect spoken in the northern and southwestern parts of China. Mandarin being the official language of China it comes as no surprise that it is the most widely spoken language in China, and it is the language of government, education, and the media.
In addition to Mandarin, there are many other languages and dialects spoken in China, some of which are completely different to standard Mandarin.
There are also many other smaller regional languages and dialects spoken in China, and some ethnic minority groups have their own languages as well. Despite the diversity of languages spoken in China, Mandarin still remains as the most commonly spoken language and is commonly used for communication between people from different parts of the country.
The answer to that question is yes, officially China is a communist country. The Chinese communist party (CCP) or officially as the Communist Party of China (CPC) has been the ruling political party in China since 1949, when the People’s Republic of China was officially established. Although they only gained power in 1949 the party was first started in 1921 with only around 50 members including Mao Zedong, it has since grown into the second largest political party in the world with well over 96.5 million members as of 2023.
The CCP is a Marxist-Leninist political party, this basically means that it is based on the ideology developed by Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin. The party’s ultimate goal is to establish a classless society in which everyone is equal and there is no exploitation of workers.
Although China, in modern times operates as more of a capitalist country it is still officially a communist government. The CCP maintains a strong monopoly on political power in China, and the government is organized according to a single-party system. The CCP has a centralized structure, with the General Secretary (Xi Jinping) of the CCP serving as the country’s top leader.


With the frequently asked questions out of the way I will now move on to 11 interesting and fun facts about China.
China is located in East Asia and is one of the world’s most populous countries, with over 1.4 billion people. China is bordered by 14 countries and the land border runs for an astounding 22 520 km (13 993 mi). The fact that China has such a long border comes as no surprise looking at their history of concurring surrounding regions and countries.
With all China’s neighbours and the size of the country itself, China has lots of different cultures and many different ethnic groups that live within its borders. This fact gives China one of the most diverse and interesting histories on the planet with the many influences of China making its way across the entire world from Asia to Europe and even Africa.
China is home to more than 1.45 billion people as of April 2023 and that number is only growing. Currently, China has the largest population on the planet, but India is expected to take the number 1 spot sometime in 2023 with some experts already agreeing that India has the largest population out of the two countries. But this information is currently unconfirmed so I will update this section when India officially has the world’s largest population.
To put China’s population into perspective, the population of China holds approximately 18.47% of the total world population. This means that nearly one out of every five people on the planet is a resident of China. China’s population has grown rapidly in recent decades, with its population more than doubling since 1950 when their population was at around 540 million. Despite government efforts to slow population growth with the one-child policy, which was later replaced with a two-child policy in 2016, and then replaced again by a 3 child policy in 2021, China remains the world’s most populous country.
However, the rate of population growth has slowed down in recent years, and the government’s family planning policies have contributed to this trend.

The population of China is distributed very unevenly across its vast territory. The most populous regions in China are along the east coast, including the cities of Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou. These regions have high population densities and are home to many of China’s largest cities.
As previously mentioned, China’s population is incredibly diverse in terms of ethnicity, with over 50 recognized ethnic groups. The majority of the population (over 90%) is Han Chinese, but there are also significant populations of ethnic minorities such as Tibetans, Uyghurs, and Mongolians.
China has a land area of approximately 9.6 million square kilometres (6.3% of the world’s total landmass), making it the third largest country in the world by land area. This is after Russia, which is the largest country in the world with a land area of over 17 million square kilometers, and Canada, which is the second largest country with a land area of almost 10 million square kilometers.
China spans approximately 5 500 km (3 400 mi) from north to south and from east to west it extends an astounding 5 000 km (3 100 miles). With China’s size it geographically speaking, spans across 5 time zones, these historically being known locally as:
But despite covering 5 time zones China has only used 1 national time zone since the CCP took power, this being Beijing time. This time zone was introduced by the Chinese government to bring unity to the country.

In the south of China, the climate is primarily tropical or subtropical, and is characterized by high temperatures with abundant rainfall throughout the year. The summer months (June to August) can be particularly hot and humid, with temperatures sometimes reaching up to 38°C (100°F) in some areas. In contrast, the winter months (December to February) are mild and sometimes cold, with temperatures ranging from 5°C to 15°C (41°F to 59°F).
In the central and eastern regions of China, including the cities of Beijing and Shanghai, the climate is classified as warm-temperate. Summers are hot and humid, with temperatures ranging from 25°C to 32°C (77°F to 90°F), while winters can be cold and dry, with temperatures dropping to -10°C (14°F) or sometimes even lower.
To the north of China, it experiences a cold-temperate climate, with long and harsh winters and short, cool summers. The temperature can drop well below -20°C (-4°F) in some areas during winter. The north western regions of China, which includes the Gobi Desert, has a desert climate, with hot summers and cold winters, and very little rainfall throughout the whole year.
And finally, the climate in China’s high altitude areas, such as the Tibetan Plateau, is characterized by low temperatures, strong winds, and low atmospheric pressure. The summer months are short and cool, with temperatures ranging from 5°C to 15°C (41°F to 59°F), while winters are long and harsh, with temperatures dropping below -20°C (-4°F). overall this is the coldest and harshest region in China.


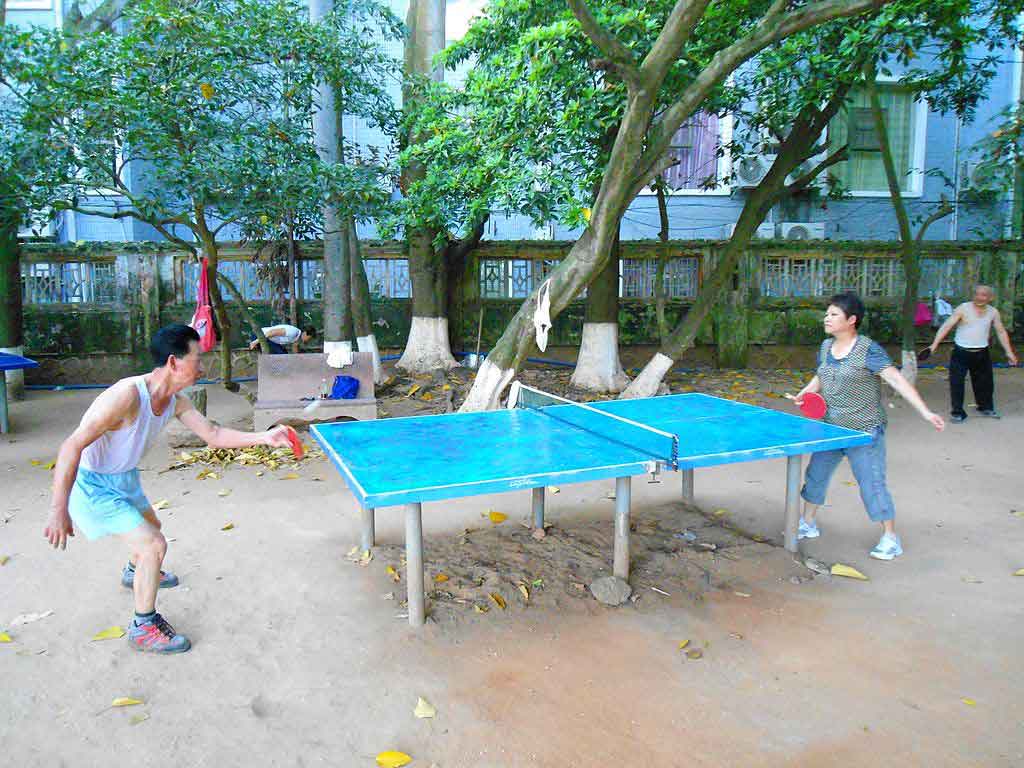
Table tennis, which is also known as ping pong, is the national sport of China and is hugely popular throughout the entire country. In case you’ve never heard of Ping Pong before, it is a fast-paced indoor game that involves two or four players hitting a lightweight ball back and forth across a table using small paddles. As the name suggests it is essentially tennis but on a table.
Table tennis has a long and rich history in China. In the 1950s and 60s, China began to dominate the sport at the international level, with players such as Rong Guotuan and Zhuang Zedong winning numerous world championships. Since then, China has become the undisputed powerhouse in the table tennis industry, with its players winning the vast majority of Olympic and world championship medals. In just the Olympics China has won 61 medals for just ping pong with 32 being Gold medals,21 Silver, and, 8 Bronze over the years.

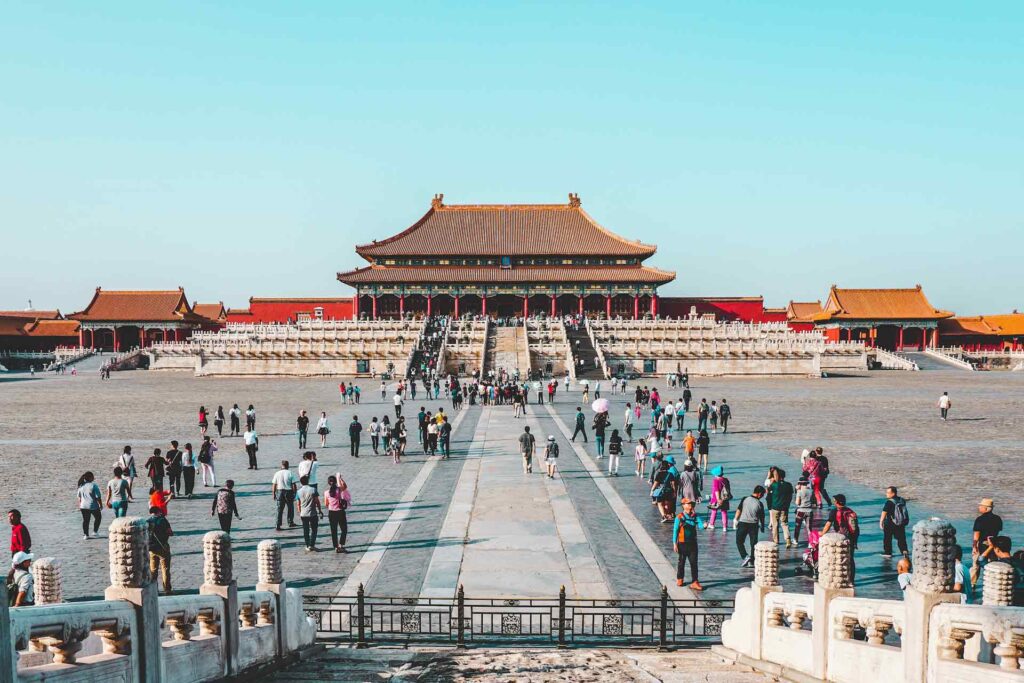
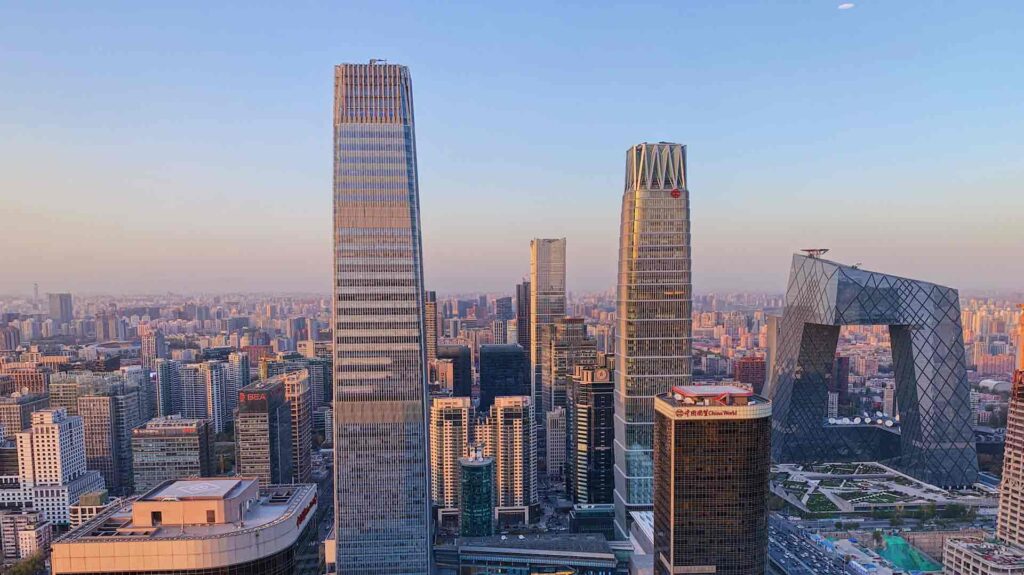
Beijing, also known in its stylized form as Peking, is the capital city of China, despite not being the largest city in terms of population. This title goes to Shanghai, with a population of over 24 million people, is China’s most populous city. Despite Shanghai’s size, Beijing remains the political and cultural center of the country.
Beijing’s history as the capital of China dates back more than 800 years. It has served as the capital of many dynasties and empires, including the Ming and Qing dynasties, as well as the Republic of China. In 1949, after the establishment of the People’s Republic of China, Beijing was declared the capital of the new communist government and has remained the capital ever since.
As of 2023, Beijing is a bustling metropolis with a population of over 21.7 million people. It is home to many of China’s most famous landmarks and attractions, including the Forbidden City, the Summer Palace, and the Great Wall of China.


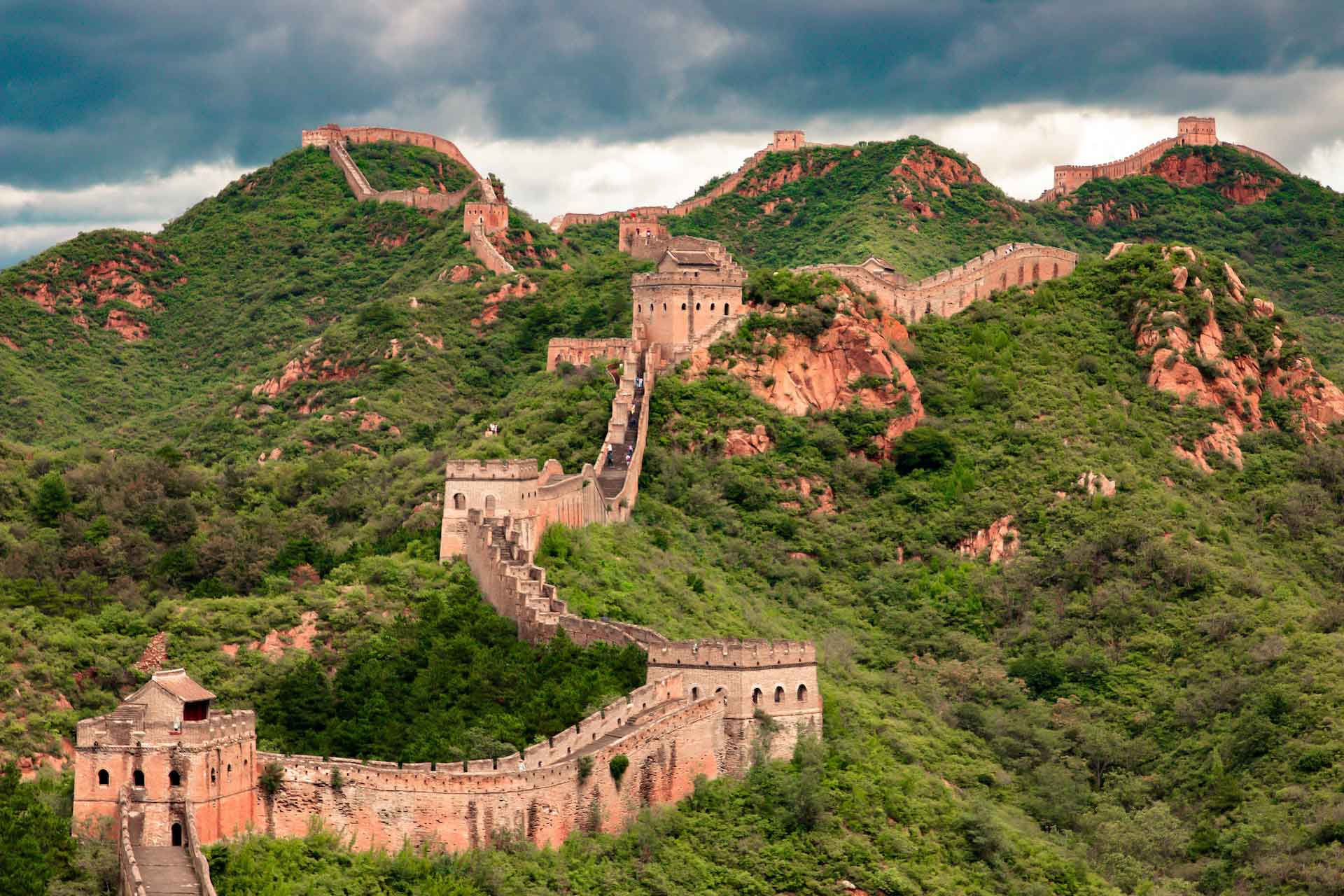
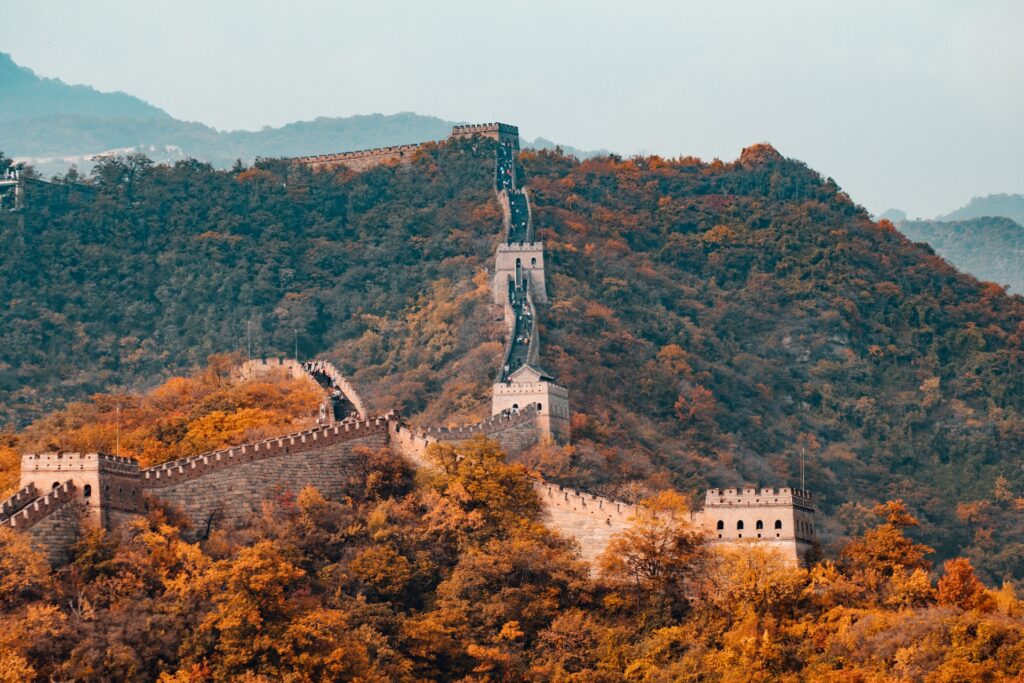
The Great Wall of China is a series of fortifications built along the northern borders of China. It was originally built to protect against invasions by Mongol tribes but eventually turned into a way to control trade in the region. It is considered one of the greatest architectural achievements in human history and is recognized as a symbol of Chinese civilization and culture.
The wall was built over a period that lasted more than 2,000 years, starting in the 7th century BC and continuing through to the Ming dynasty (1368-1644 AD). The wall runs a total length of 21 196 kilometers (13 171miles) across China, from Shanhaiguan in the east to Jiayuguan in the west, making it the longest wall in the world.
Despite its incredible length it is possible to walk the entirety of the walk. Although the walk is hard, long, and, treacherous it has been done by a few people in the past. The trek would end up taking somewhere around 18 months depending on your paise and the current condition of the wall as a lot of the wall that wasn’t built in the Ming dynasty is unfortunately crumbling.

China has a long history of invention and innovation, with many important inventions and discoveries that affected the entire planet being credited to the Chinese people. Among these, perhaps the most significant discoveries are paper, gunpowder, the compass, and printing.
Paper is believed to have been invented in China during the Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD), using a mixture of mulberry bark, hemp, and rags. The invention of paper was a crucial development in the history of humanity as it made writing and reading material much more accessible and affordable for the general population.
Gunpowder, which is a mixture of saltpeter, sulfur, and charcoal, was also invented in China during the Tang dynasty (618 – 907 AD). Originally it was used for fireworks and as a fun item to be used during peace, but gunpowder soon found its way into military applications, including the development of early firearms such as the fire lance and the hand cannon.
The compass, which is used for navigation and orientation, was also invented in China during the Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) The earliest compasses were made from lodestone, a naturally occurring magnetic mineral.
Printing, which is the process of reproducing text and images using a printing press, was also invented in China during the Tang dynasty (618-907 AD). The earliest printing methods involved carving text or images onto woodblocks, which were then inked and pressed onto paper. This process was much faster and more efficient than hand-copying and paved the way for the mass production of books and other printed materials.
According to Chinese folk law, tea was first discovered by Emperor Shen Nong, who was supposedly the first emperor of ancient China around 5 000 years ago. The story goes that while the emperor was boiling water one day, some tea leaves accidentally fell into the pot. Intrigued by the resulting infusion, he tasted it and found it to be refreshing and invigorating. From then on, he began to promote the consumption of tea as a medicinal beverage.
While this legend may not be entirely true, there is historical evidence to suggest that tea has been consumed in China for at least the last 2 000 years. The earliest written reference to tea dates back to the Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD), when it was used as a medicinal herb. Over time, tea became a popular beverage in China, with many different varieties and formals emerging to suit different tastes and preferences.
Today, China remains one of the largest producers and consumers of tea in the world, with a rich and diverse tea culture that has evolved over thousands of years.


The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) is the military organization of the People’s Republic of China, and it is responsible for defending China’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. The PLA is the largest and one of the most powerful military forces in the world, with over 2 million active personnel and an additional 2 million personal in other paramilitary and in reserve as of 2023.
In addition to its active personnel, the PLA also has a large arsenal of weapons and military equipment, including tanks, aircraft, warships, and ballistic missiles.
China’s economy has been growing rapidly in recent decades, with an average annual growth rate of around 10% since the 1980s. In 2010, China overtook Japan as the world’s second-largest economy in terms of nominal GDP, and since then, it has remained in that position.
As of 2021, China’s nominal GDP is estimated to be around $16.4 trillion, making it the second-largest economy in the world after the United States, which has a nominal GDP of around $22.7 trillion. However, when it comes to purchasing power parity (PPP), which takes into account the differences in prices between countries, China is the largest economy in the world, with a PPP-adjusted GDP of around $24.8 trillion, compared to the United States PPP-adjusted GDP of around $22.7 trillion.
In conclusion, China is a fascinating country with a rich and diverse culture, history, and geography. From the iconic landmarks like the Great Wall of China to the beautiful forbidden city it has a lot of manmade beauties to experience as well as many natural ones. With its long history of invention and innovation, China has made many important contributions to human civilization, including the invention of paper, gunpowder, the compass, and printing. Whether you’re interested in art, history, science, or adventure, China is sure to have something to captivate your imagination.

If you enjoyed this article and would like to see more please click below to see a similar article about another interesting country.
Related post: Iran: Fun Facts about a country once known as The Persian Empire!